此博客持续更新,旨在记录一些重点、易错点、遗忘点以及二次元美图。
基操勿6
stdIO
整数输入输出:
int a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
cout << a + b << endl;字符串:
string str;
cin >> str;
cout << str;cout << “woof” << endl; 与 cout << “woof\n”; 等同。
格式化输出 - 小数/科学计数法/字符串の限位:
cout << format( “{:.2f} {:.3e} {:.4s}\n", 3.14159, 12345.678, "abcdef") << endl;
// 输出:3.14 1.235e+04 abcd输出地址:
char c = 'a';
cout << (void*)&c << endl;
// output: 0x971c1ff99fstring的比较:
>, <, >=, <=, ==, !=
传参:
1):main()外部调用main()内部参数时,参数改动不影响其真实值。
2):外部调用内部参数时,参数值同步改变。
数组:
*a == a[] == a[LENGTH];多维数组形参除第一维外,其余必须指定。
// 访问数组元素的不同方法
int arr[5] = {1,2,3,4,5};
int *ptr = arr;
// 三者等同:
cout << arr[3];
cout << *(ptr+3);
cout << ptr[3];条件运算符?:
condition ? consequent : alternative
condition 表达式的计算结果必须为 true 或 false。 若 condition 的计算结果为 true,将计算 consequent,其结果成为运算结果;若 condition 的计算结果为 false,将计算 alternative,其结果成为运算结果。
类与结构体:
类:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Person {
private:
int age, height;
double money;
string books[100];
public:
string name;
Person(string _name, int _age) {
name = _name;
age = _age;
money = 1000;
}
Person(string _name, int _age, double _money) : name(_name), age(_age), money(_money) {}
void say() {
cout << "I'm " << name << endl;
}
void add_money(double x) {
money += x;
}
void set_age(int x) {
age = x;
}
};
int main() {
class Person c("yxc", 18, 10086);
c.name = "qbt";
c.set_age(18);
c.add_money(10000);
c.say();
return 0;
}
// output:
// I'm qbt结构体:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Person {
int age, height;
double money;
string books[100];
string name;
Person(string _name, int _age) {
name = _name;
age = _age;
money = 1000;
}
Person(string _name, int _age, double _money) : name(_name), age(_age), money(_money) {}
void say() {
cout << "I'm " << name << endl;
}
void add_money(double x) {
money += x;
}
void set_age(int x) {
age = x;
}
};
int main() {
class Person c("yxc", 18, 10086);
c.name = "qbt";
c.set_age(18);
c.add_money(10000);
c.say();
return 0;
}
// output:
// I'm qbtclass默认变量,struct默认;
两者构造差不多,上述示例做参考。
数据结构()
链表
// define
struct Node {
int val; Node* next;
}
int main() {
Node *node = new Node(1); // 正确,此处传引用
Node *node = Node(1); // 错误,此处指Node型变量,传值
}- 头节点:节点的,即
head指向的就是其后节点的地址,不用head->next!
堆/栈
RAM Space
·-----------------·
Stacks | | func() call; |
(Downwards) | | local val…… |
| | |
↓ | |
| |
|`````````````````|
Heaps ↑ | global val…… |
(Upwards) | | |
| | |
| | |
·-----------------·- 栈:后进先出(文件柜)多用于深度优先搜寻
- 队列:先进先出(羽毛球筒)多用于广度优先搜寻
STL
#include <vector>
vector是变长数组,支持随机访问,不支持在任意位置 O(1) 插入。为了保证效率,元素的增删一般应该在末尾进行。
- Declare:
#include <vector> // 头文件
vector<int> a; // 相当于一个长度动态变化的int数组
vector<int> b[233]; // 相当于第一维长233,第二位长度动态变化的int数组
struct rec{…};
vector<rec> c; // 自定义的结构体类型也可以保存在vector中size/empty
size函数返回vector的实际长度(包含的元素个数),empty函数返回一个bool类型,表明vector是否为空。二者的时间复杂度都是O(1)。
所有的STL容器都支持这两个方法,含义也相同,之后我们就不再重复给出。
clear
clear函数会清空vector容器。
- 迭代器
迭代器就像STL容器的“指针”,可以用星号*操作符解除引用。
一个保存int的vector的迭代器声明方法为:
vector<int>::iterator it;若想直接访问迭代器的值,需要在变量前加* 例如*i。
vector的迭代器是“随机访问迭代器”,可以把vector的迭代器与一个整数相加减,其行为和指针的移动类似。可以把vector的两个迭代器相减,其结果也和指针相减类似,得到两个迭代器对应下标之间的距离。
begin/end
begin函数返回指向vector中第一个元素的迭代器。例如a是一个非空的vector,则*a.begin()与a[0]的作用相同。
所有的容器都可以视作一个“前闭后开”的结构,end函数返回vector的尾部,即第n个元素再往后的“边界”。*a.end()与a[n]都是越界访问,其中n = a.size()。
下面两份代码都遍历了vector<int> a,并输出它的所有元素。
for (int i = 0; i < a.size(); i ++)
cout << a[i] << endl;
for (vector<int>::iterator it = a.begin(); it != a.end(); it ++)
cout << *it << endl;front/back
front函数返回vector的第一个元素,等价于*a.begin()和a[0]。 back函数返回vector的最后一个元素,等价于*--a.end()和a[a.size() – 1]。
push_back()和pop_back()
a.push_back(x)把元素x插入到vector a的尾部。 b.pop_back()删除vector a的最后一个元素。
来源https://www.acwing.com/file_system/file/content/whole/index/content/3598249/
技巧
- 定义空(
NULL)时,使用nullptr更好! - 使用下列代码来减少带
cin/cout代码的运行时间消耗:
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);好题共赏
动物
给定你三个葡萄牙语单词,这些词将根据下表从左到右定义一个动物。 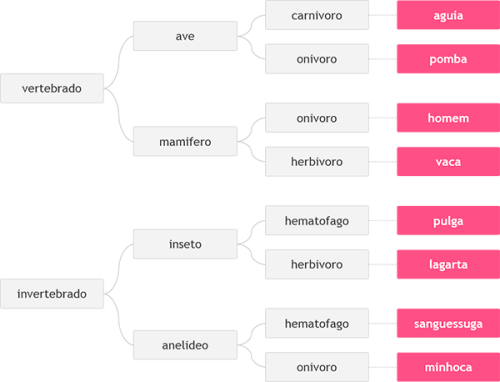 OI 请你确定并输出这个动物的名称。
OI 请你确定并输出这个动物的名称。
输入格式
根据上表,输入包含三个单词,每行一个,用以识别动物,单词由小写字母构成。
输出格式
输出识别出的动物的名称。
- 输入样例:
vertebrado
mamifero
onivoro- 输出样例:
homem题解:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string s[3]; string sF;
for(int i=0; i<3; i++) {
cin>> s[i]; sF+= s[i][0];
}
if(sF=="vac") cout<< "aguia";
if(sF=="vao") cout<< "pomba";
if(sF=="vmo") cout<< "homem";
if(sF=="vmh") cout<< "vaca";
if(sF=="iih") {
if(s[2] == "hematofago") cout<< "pulga";
else cout<< "lagarta";
}
if(sF=="iah") cout<< "sanguessuga";
if(sF=="iao") cout<< "minhoca";
}点的坐标
给定两个保留一位小数的浮点数X,Y,用来表示一个点的横纵坐标。 请你判断该点在坐标系中的位置。
输入格式
共一行,包含两个浮点数X,Y,表示点的横纵坐标。
输出格式
如果点在第一象限,则输出 Q1,在第二象限,则输出 Q2,以此类推。
如果点在原点处,则输出 Origem。
否则,如果点在x坐标上,则输出 Eixo X,在y坐标上,则输出 Eixo Y。
数据范围 -10.0≤X,Y≤10.0
- 输入样例1:
4.5 -2.2- 输出样例1:
Q4- 输入样例2:
0.0 0.0- 输出样例2:
Origem题解
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
double x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
if (x == 0 && y == 0) cout << "Origem";
else if (x * y == 0) cout << (x == 0 ? "Eixo X" : "Eixo Y");
else if (x > 0) cout << (y > 0 ? "Q1" : "Q4");
else cout << (y > 0 ? "Q2" : "Q3");
return 0;
}C++,危险又优雅~  cum!
cum!
